
RTCA/DO-160
RTCA/DO-160 Section 20: Radio Frequency Susceptibility (Conducted/Radiated)
Standard Overview
RTCA/DO-160 Section 20 provides test procedures to determine if equipment will operate when the EUT and its interconnecting cables are exposed to Radio Frequency interference. Continuous Wave (CW), Square Wave AM (SW), and Pulse Modulated (PM) RF signals are required. A Line Impedance Stabilization Network (LISN) must be inserted in series with each power lead and ungrounded power return lead, with a 10 uF capacitor connected between the power input of the LISN and the ground plane.
RTCA/DO-160 Section 20 has been updated to reflect the requirements of the new FAA rule for High Intensity Radiated Fields testing, also known as HIRF Testing, which is a form of EMC testing applicable to equipment that is subject to extreme electromagnetic environments and/or mission-critical equipment whose failure would be hazardous to human safety. HIRF requirements are applied to ensure that the aircraft electrical and electronic systems can continue safe operation without interruption, failure or malfunction.
During testing, the RF current induced into the cable or lead under test is monitored with a calibrated RF current probe, and the RF power applied to the injection probe is increased until the appropriate current level (as defined by the applicable Equipment Category used) is reached.
_20.png)
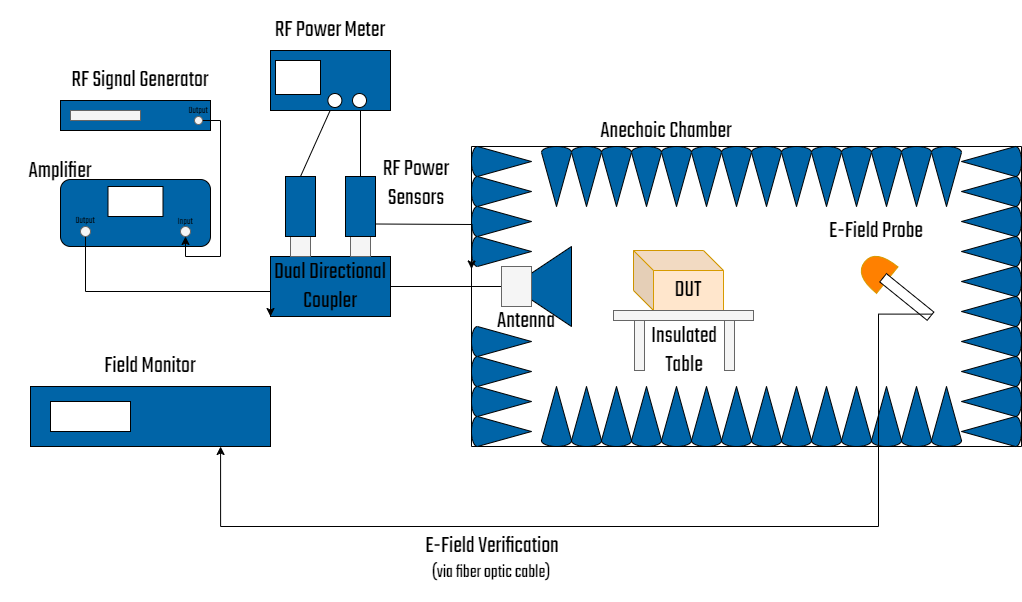
There two RF radiated susceptibility test methods specified in RTCA/DO-160 Section 20. The first method uses a standard semi-anechoic chamber as in MIL-STD-461F test method RS103 and requires the chamber to be lined with an RF absorber of a specified minimum performance. The minimum antenna distance is normally 1 meter, and multiple antenna positions are required when the beamwidth of the antenna does not completely cover the system. The RF power applied to the antenna input, that is required to achieve the specified test level, is recorded for each antenna used. During EUT testing, the calibrated power level for each test frequency is applied to the antenna.
The second method uses a Reverberation Chamber, which requires a Field Uniformity Validation and Maximum Chamber Loading Verification before the first use of the chamber, or after any modifications. Field Uniformity measurements are performed with a 3-axis E-Field probe at up to nine different positions within the chamber. Additionally, a passive, linear, monitor antenna is moved to different positions within the chamber to calibrate the monitor antenna for use before each test. This calibration allows the monitor antenna to be used to measure Chamber Q, Time Constant, and Test Level determination, during EUT testing.
The RF power level required to achieve the desired test level for each test frequency is determined by injecting a known RF power level (typically 1 watt) into the chamber, and then measuring the field level inside the Reverb Chamber with the monitor antenna, after the EUT installed in the chamber.
RTCA/DO-160 provides standard procedures and environmental test criteria for testing airborne equipment for the entire spectrum of aircraft from light, general aviation aircraft and helicopters through the "jumbo jets" and SST categories of aircraft. The tests outlined in this standard are performed to meet FAA and international regulations for electrical and electronic equipment installed on commercial aircraft.
RTCA/DO-160 G is the current version of this standard. Coordinated with EUROCAE, RTCA/DO-160G and EUROCAE/ED-14G are identically worded. DO-160G is recognized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as de facto international standard ISO-7137.
RTCA/DO-160 Section 20 has been updated to reflect the requirements of the new FAA rule for High Intensity Radiated Fields testing, also known as HIRF Testing, which is a form of EMC testing applicable to equipment that is subject to extreme electromagnetic environments and/or mission-critical equipment whose failure would be hazardous to human safety. HIRF requirements are applied to ensure that the aircraft electrical and electronic systems can continue safe operation without interruption, failure or malfunction.
Conducted Susceptibility
Similar to MIL-STD-461F test method CS114, the RF conducted susceptibility test has the RF interference coupled into the EUT interconnecting cables and power leads using an injection probe calibrated (in a 50 ohm fixture) to the required test level before performing the test.During testing, the RF current induced into the cable or lead under test is monitored with a calibrated RF current probe, and the RF power applied to the injection probe is increased until the appropriate current level (as defined by the applicable Equipment Category used) is reached.
Radiated Susceptibility
Similar to MIL-STD-461F test method RS103, the EUT and its interconnecting cables and power leads are exposed to RF radiated fields in the frequency range of 100 MHz to 18 GHz._20.png)
There two RF radiated susceptibility test methods specified in RTCA/DO-160 Section 20. The first method uses a standard semi-anechoic chamber as in MIL-STD-461F test method RS103 and requires the chamber to be lined with an RF absorber of a specified minimum performance. The minimum antenna distance is normally 1 meter, and multiple antenna positions are required when the beamwidth of the antenna does not completely cover the system. The RF power applied to the antenna input, that is required to achieve the specified test level, is recorded for each antenna used. During EUT testing, the calibrated power level for each test frequency is applied to the antenna.
The second method uses a Reverberation Chamber, which requires a Field Uniformity Validation and Maximum Chamber Loading Verification before the first use of the chamber, or after any modifications. Field Uniformity measurements are performed with a 3-axis E-Field probe at up to nine different positions within the chamber. Additionally, a passive, linear, monitor antenna is moved to different positions within the chamber to calibrate the monitor antenna for use before each test. This calibration allows the monitor antenna to be used to measure Chamber Q, Time Constant, and Test Level determination, during EUT testing.
The RF power level required to achieve the desired test level for each test frequency is determined by injecting a known RF power level (typically 1 watt) into the chamber, and then measuring the field level inside the Reverb Chamber with the monitor antenna, after the EUT installed in the chamber.
Equipment Categories
Equipment Category designation for Section 20 consists of two letters. Conducted susceptibility test levels are designated with the first category character and radiated susceptibility test levels with the second category character. There are 7 Equipment Categories for conducted susceptibility, and 10 Equipment Categories for radiated susceptibility. These categories indicate the severity level of the tests performed, and/or the type of modulation used.RTCA/DO-160 provides standard procedures and environmental test criteria for testing airborne equipment for the entire spectrum of aircraft from light, general aviation aircraft and helicopters through the "jumbo jets" and SST categories of aircraft. The tests outlined in this standard are performed to meet FAA and international regulations for electrical and electronic equipment installed on commercial aircraft.
RTCA/DO-160 G is the current version of this standard. Coordinated with EUROCAE, RTCA/DO-160G and EUROCAE/ED-14G are identically worded. DO-160G is recognized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) as de facto international standard ISO-7137.
Products Used in Testing

Empower 2208 Solid State Pulse Amplifier
- Frequency Range: 1 - 2GHz
- Output: 8kW, 69dB
- Duty Cycle: 10%, Pulse Width: 1 - 5μs


Amplifier Research 2500A225 RF Power Amplifier | 2500 Watt CW, 10 kHz – 225 MHz
- Equipped with a Digital Control Panel (DCP) which provides local and remote control of the amplifier
- Remote control: Ethernet, USB, GPIB, fiber-optic serial, RS-232
- Push-pull LDMOS circuitry is utilized in all high power stages in the interest of low distortion and improved stability

-compressed_24.jpg?width=400)
Advanced Amplifiers AA-12G-4KWP Pulsed Amplifier
- Frequency Range: 1.0 - 2.0GHz
- Output: 4kW, 66dBm
- Duty Cycle: 6%, Pulse Width: up to 100μs


Advanced Amplifiers AA-80M1G-1000 Solid State Amplifier
- 80.0 MHz - 1.0 GHz
- 1000 W
- 60 dB min


Advanced Amplifiers AA-618G-300 Solid State Amplifier
- 6.0 - 18.0 GHz
- 300 W
- 55 dB min


Advanced Amplifiers AA-700M6G-300 Solid State Amplifier
- 0.7 - 6.0 GHz
- 300 W
- 53 dB min


Bruel & Kjaer 4535-B-001 Triaxial Accelerometer
- Single axis supply makes single- or bi-axial measurement possible to save channels
- Wide frequency range from 0.3 Hz to 10 kHz on all three axes
- Low noise for structural testing


Rohde & Schwarz ESW44 | 1 Hz – 44 GHz
- Standard-compliant EMI measurements in spectrum analyzer mode
- RF performance that meets exacting demands
- Exceptionally wide dynamic range


GAUSS INSTRUMENTS TDEMI ULTRA40 | 9 kHz – 40 GHz
- A frequency range from DC up to 40 GHz
- 685 MHz real-time analysis bandwidth
- Dynamic range of more than 100 dB


AE Techron 8704 Linear Power Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 250 kHz
- Gain: 20V
- Max Power Output: Up to 4 kW continuous


AE Techron 7228 Linear Power Amplifier
- DC – 1 MHz
- Gain: 20V
- AC Power: 1000W RMS


AE Techron 7782 RMS Power Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 50 kHz at full power
- Gain: 20V
- Max Power Output: 3305 W RMS (2 Ω)


AE Techron 7136 AC/DC Amplifier with Precision DC Power Supply
- Frequency Range: DC – 150 kHz
- Gain: 40 V
- Max Power Output: 900 W RMS (AC)


AE Techron 9110 Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 250kHz (–3 dB)
- Gain: 20V
- Max Power Output: 5kW


AE Techron 7796 DC Power Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 50kHz (rated) | DC – 100kHz (reduced)
- Gain: 20V
- Max Power Output: 22,000 W peak (40 mSec, 0.5 Ω load)


AE Techron 7794 4-Quadrant Power Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 150 kHz
- Gain: 20 V
- Max Power Output: 5,000 W RMS (continuous)


AE Techron 7224 Linear Power Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 300 kHz
- Gain: Voltage Mode: 20 V
- Max Output Power: 1,100 W RMS


AE-Techron 7796HC DC Power Amplifier
- Frequency Range: DC – 150 kHz
- Gain: 20 V
- Max Power Output: 2,499 W RMS continuous


AE Techron 8500 Series Amplifiers | DC to 50 kHz, 60 to 300 ARMS
- Bandwidth: DC to 50 kHz
- Current: 60 to 300 ARMS
- For Mil-PRF capacitor tests, DC automotive dropout testing, and as a variable AC source for ISO 61000, Aviation and Power Quality Measurements.


BOLAB 100-TS Series | DC up to 1 MHz, 400 W – 18000 W
- Bandwith: DC up to 1 MHz
- Output: 400 W – 18000 W
- For LV124 / VW80000, LV148, ISO 16750, ISO 7637, DIN 40839, and GS 95024


BOLAB Systems BLS-130-70N-TS 4-Quadrant Voltage Amplifier
- DC up to 1 MHz (small signal -3 dB)
- Ouput: 3,000 W
- For LV124 / VW80000, LV148, ISO 16750, ISO 7637, DIN 40839, GS 95024
