ICNIRP 2010 is the latest version of a set of guidelines established by ICNIRP, an internationally recognized standards body that defines requirements for protection against non-ionizing radiation. This edition improves on its 1998 predecessor by replacing the simple geometrical models used for measuring radiation absorption with detailed computational simulations that are anatomically accurate. ICNIRP 2010 also revises basic restrictions and dosimetric models employed in reference levels; magnetic field reference levels tend to be less conservative whereas electric field levels remain the same.
ICNIRP 1998 is the previous version of this standard. The 1998 edition covers a wider frequency range of 0 - 300 GHz.

Non-ionizing radiation affects the central nervous system at low frequencies and the peripheral nervous system at high frequencies, incurring sensory changes and a physical heating of the body respectively. According to ICNIRP, the following symptoms of electromagnetic exposure serve as the basis for EMF safety guidelines:
- The perception of surface charge
- The experience of retinal magnetic phosphenes (flickering lights on the edges of one’s vision)
- The direct stimulation of nerve and muscle tissue
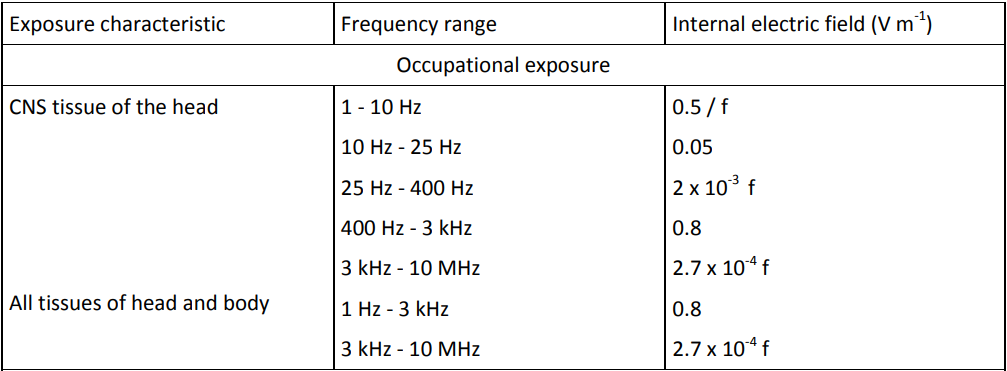
Occupational Exposure
- 10 kHz – 25 Hz: Exposure should be limited to electric field strengths of less than 50 mV m-1 in CNS tissue of the head to avoid magnetic phosphenes and other transient effects on the brain
- Up to 400 Hz: Limit value rises proportional to frequency
- 400 Hz – 3 kHz: Exposure should be limited to electric field strengths of less than 800 mV m-1 in all parts of the body to avoid nerve stimulation
- Above 3 kHz: Limit value rises proportional to frequency
- Controlled Environments, 1 – 400 Hz: Exposure should be limited to electric field strengths of less than 800 mV m-1 in all parts of the body to avoid both CNS and PNS stimulation
Basic Restrictions
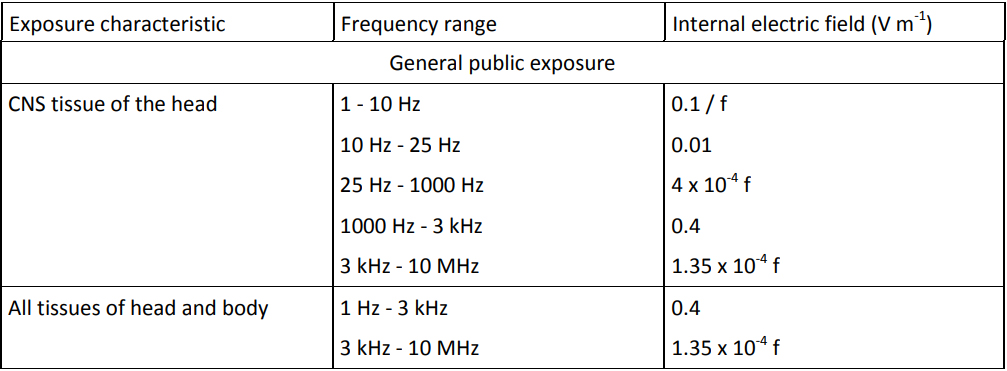
General Public Exposure
- 10 Hz – 25 Hz: Exposure should be limited to electric field strengths of less than 10 mV m-1 in CNS tissue of the head to avoid magnetic phosphenes and other transient effects on the brain. The basic restriction rises both above and below this frequency range.
- 1 kHz: Exposure should be limited to electric field strengths of less than 400 mV m-1 in all parts of the body to avoid nerve stimulation
Basic Restrictions
 Download ICNIRP 2010 PDF
Narda STS SRM-3006: Selective Measurements for ICNIRP
Download ICNIRP 2010 PDF
Narda STS SRM-3006: Selective Measurements for ICNIRP